위로
아래
File 클래스
- 파일이나 폴더의 경로를 추상화한 클래스
- java.io 패키지에 포함되어 있다.
File 클래스 생성자
- FIle(File parent, String child) : parent 객체 폴더의 chiled라는 File 객체를 생성한다.
- FIle(String pathname) : parthnme에 해당하는 File 객체를 생성한다.
- File(String parent, String child) : parent 폴더에 child라는 File 객체를 생성한다.
- File(URI uri) : uri 경로에서 File객체를 생성한다.
주요 메소드
- canExcute() : 실행 가능한 파일인지 여부를 boolean으로 반환
- canRead() : 읽을 수 있는 파일인지 여부를 boolean으로 반환
- canWrite() : 쓸 수 있는 파일인지 여부를 boolean으로 반환
- createNewFile() : 파일을 새로 생성하면 ture, 아니면 false 반환
- delete() : 파일을 삭제하면 true, 아니면 false 반환
- exists() : 파일의 존재 유무를 boolean으로 반환
- getAbsolutePath() : 파일의 절대 경로를 반환한다.
- getName() : 파일의 이름을 반환
- getPath() : 파일의 경로를 반환
- isDirectory() : 폴더의 존재 유무를 boolean으로 반환
- isFile() : 파일 존재 유무를 boolean으로 반환
- lastModified() : 파일의 마지막 수정 시간을 반환 (long)
- length() : 파일의 크기를 반환 (long)
- list() : 모든 자식 파일과 폴더를 문자열 배열로 반환 (String[] )
- listFIles() : 모든 자식 파일과 폴더를 File 배열로 반환 (File[])
- mkdir() : 폴더를 생성하면 true, 아니면 relse
- toPath() : 파일 경로에서 구성한 Path 객체를 반환 (Path)
예시
더보기
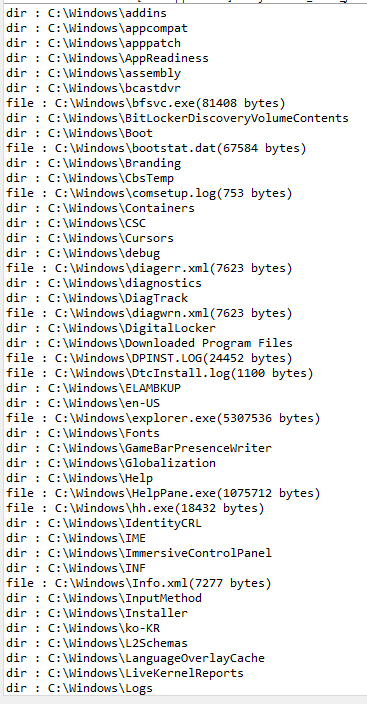
import java.io.*;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FileDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
File file = new File("C:\\Windows");
File[] fs = file.listFiles();
for(File f : fs)
if(f.isDirectory())
System.out.printf("dir : %s\n", f);
else
System.out.printf("file : %s(%d bytes)\n", f, f.length());
}
}
Path 인터페이스와 FIles 클래스
Path인터페이스
- File 클래스(운영체제에 따라 일관성 없이 작동)을 대체한다.
- 기존 FIle 객체도 toPath() 메소드를 이용해 Path 타입으로 올 수 있다.
- Path 인터페이스의 구현 객체는 파일 시스템에서 경로를 나타낸다.
- 주요 메소드
- getFileName() : 객체가 가리키는 파일(폴더) 이름을 반환 (Path)
- getFileSystem() : 객체를 생성한 파일 시스템을 반환 (FileSystem)
- getNameCount() : 객체가 가리키는 경로의 구성 요소 개수를 반환 (int)
- getParent() : 부모 경로를 반환. 없으면 null 반환 (Path)
- getRoot() : 루트를 반환. 없으면 null 반환 (Path)
- isAbsolute() : 절대 경로 여부를 반환 (boolean)
- toAbsolutePath() : 절대 경로를 나타내는 객체를 반환 (Path)
- toUri() : 객체가 가리키는 경로에서 URI를 반환 (URI)
Files 클래스
- FIles 클래스는 파일 연산을 수행하는 정적 메소드로 구성되어 있다.
- 주요 메소드
- copy() : 파일을 복사한 후 복사된 바이트 개수 반환 (long)
- copy() : 파일을 복사한 후 복사된 경로를 반환 (Path)
- createDirectory() : 폴더를 생성 (Path)
- createFile() : 파일을 생성 (Path)
- delete() : 파일을 삭제 (void)
- deleteIfExists() : 파일이 있으면 삭제 (boolean)
- exists() : 파일의 존재 유무를 조사 (boolean)
- isDirectory() : 폴더인지 조사 (boolean)
- isExecutable() : 실행 가능한 파일인지 조사 (boolean)
- isHidden() : 숨김 파일인지 조사 (boolean)
- isReadable() : 읽기 가능한 파일인지 조사 (boolean)
- isWritable() : 쓰기 가능한 파일인지 조사 (boolean)
- move() : 파일 이동(Path)
- notExists() : 파일(폴더)의 부재 조사 (boolean)
- readAllBytes() : 파이르이 모든 바이트를 읽어 배열로 반환 (byte[])
- readAllLines() : 파일의 모든 행을 읽어 리스트로 반환 (List<String>)
- size() : 파일의 크기를 반환 (long)
- write() : 파일에 데이터를 쓴다. (Path)
예시
더보기
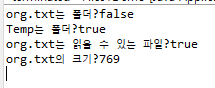
import java.io.File;
import java.nio.file.Files;
public class Files1Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
File f1 = new File("D:\\Temp\\org.txt");
File f2 = new File("D:\\Temp");
System.out.println("org.txt는 폴더?" + Files.isDirectory(f1.toPath()));
System.out.println("Temp는 폴더?" + Files.isDirectory(f2.toPath()));
System.out.println("org.txt는 읽을 수 있는 파일?" + Files.isReadable(f1.toPath()));
System.out.println("org.txt의 크기?" + Files.size(f1.toPath()));
}
}

예시
더보기
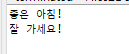
import java.io.*;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.nio.file.*;
import java.util.List;
public class Files2Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Charset cs = Charset.defaultCharset();
Path p = new File("D:\\Temp\\new.txt").toPath();
if(Files.notExists(p))
Files.createFile(p);
byte[] data = "좋은 아침!\n잘 가세요!\n".getBytes();
Files.write(p, data, StandardOpenOption.APPEND);
try {
List<String> lines = Files.readAllLines(p,cs);
for(String line : lines)
System.out.println(line);
} catch(IOException e) {}
}
}
스트림 생성
- BufferedReader 클래스의 lines() 메소드를 이용하면 스트림을 생성할 수 있다.
- File 객체의 배열도 Stream<File>이라는 스트림을 생성할 수 있다.
- Files 클래스가 제공하는 스트림을 반환하는 정적 메소드 종류
- Stream<String> lines(Path path) : 기본 문자집합을 이요해 파일의 모든 행을 스트림으로 반환
- Stream<String> lines(Path path, Charset cs) : 주어진 문자집합을 이용해 파일의 모든 행을 스트림으로 반환
- Stream<Path> list(Path dir) : 서브 폴더를 제외한 폴더에 들어 있는 모든 원소를 스트림으로 반환
- Stream<Path> walk(Path start) : 서브 폴더를 포함한 폴더에 들어 있는 모든 원소를 스트림으로 반환
예시
더보기

import java.io.*;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
public class Stream1Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("C:\\Windows");
File[] fs = file.listFiles();
Stream<File> stream = Arrays.stream(fs);
long count = stream.filter(x -> x.isDirectory()==false).count();
System.out.println("C:\\Windows에 있는 파일 개수 : " + count);
}
}
예시
더보기
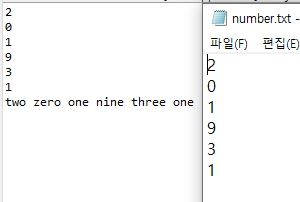
package IO;
import java.io.File;
import java.nio.file.*;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
public class Stream2Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//2, 0, 9, 1, 3, 1 파일에 한 줄씩저장
//마지막 엔터 치면 오류남 (마지막 엔터를
String[] number = {"zero","one","two","three","four","five","six","seven","eight","nine"};
Path p = new File("D:\\Temp\\number.txt").toPath();
Stream<String> s = Files.lines(p);
//Files.lines(p)는 한 줄씩 읽는다.
s.forEach(x -> System.out.println(x));
s = Files.lines(p);
//마지막 엔터가 '\n'로 입력되어서 Integer.parseInt(x)를 거치면 오류난다.
s.map(x->number[Integer.parseInt(x)])
.forEach(x -> System.out.print(x+" "));
}
}
버퍼
Buffer(버퍼)
- NIO 기반의 데이터 입출력을 위해 사용되는 메모리 배열
- java.nio 패키지에 있는 추상 클래스
- capacity : 버퍼의 크기
- limit : 읽거나 쓰기 위한 버퍼 위치의 한계값
- position : 자료구조에서의 위치
- 버퍼에 전달할 데이터는 배열 타입이며, get(), put() 메소드로 전달한다.
- 종류 : ByteBuffer, CharBuffer, DoubleBuffer, FloatBuffer, IntBuffer, LongBuffer, ShortBuffer
- 메소드 종류
- allocate() 메소드 : 버퍼를 생성
- array() : 배열로 반환한다 (Object)
- capacity() : capacity 값을 반환한다. (int)
- clear() :
- flip() : position = 0으로 설정.
- limit() : limit 값을 반환 (int)
- position() : position 값을 반환. 인덱스 값으로 0부터 시작. (int)
- rewind() :
예시
더보기
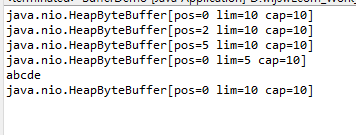
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
public class BufferDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(10);
System.out.println(buf);
buf.put("ab".getBytes());
System.out.println(buf);
buf.put("cde".getBytes());
System.out.println(buf);
buf.flip();
System.out.println(buf);
System.out.println(new String(buf.array()));
buf.clear();
System.out.println(buf);
}
}
파일 채널
FileChannel (파일 채널)
- NIO 기반의 데이터 흐름을 위한 수단을 제공하려는 클래스
- IO 기반의 입출력 스트림과는 달리, 입출력 양방향을 지원
- 기본적으로 버퍼를 이용한다.
- java.nio.channels 패키지에 있다.
- 추상 클래스로서, 동기화 처리가 되어 있어서 다중 스레드 환경에서도 안전하다.
- 소용량 파일을 처리할 때 빠르다. (대용량은 IO 기반이 낫다)
예시
더보기
import java.io.*;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
import java.nio.file.*;
public class Channel1Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D:\\Temp\\org.txt");
Path path = Paths.get("D:\\Temp\\dup.txt");
FileChannel org = fis.getChannel();
FileChannel dup = FileChannel.open(path, StandardOpenOption.WRITE,StandardOpenOption.CREATE);
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(10);
while (org.read(buf)!=-1) {
buf.flip();
dup.write(buf);
buf.clear();
}
org.close();
dup.close();
}
}
예시
더보기
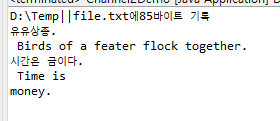
package IO;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
import java.nio.file.*;
import java.nio.file.StandardOpenOption;
public class Channel2Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Path p = Paths.get("D:\\Temp\\data.txt");
FileChannel fc = FileChannel.open(p,
StandardOpenOption.READ,
StandardOpenOption.CREATE,
StandardOpenOption.WRITE);
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
String s ="유유상종.\n Birds of a feater flock together.\n" + "시간은 금이다.\n Time is money.";
buf.put(s.getBytes());
buf.flip();
int count = fc.write(buf);
System.out.println("D:\\Temp||file.txt에" + count + "바이트 기록");
buf.clear();
fc.read(buf);
System.out.println(new String(buf.array()));
fc.close();
}
}
